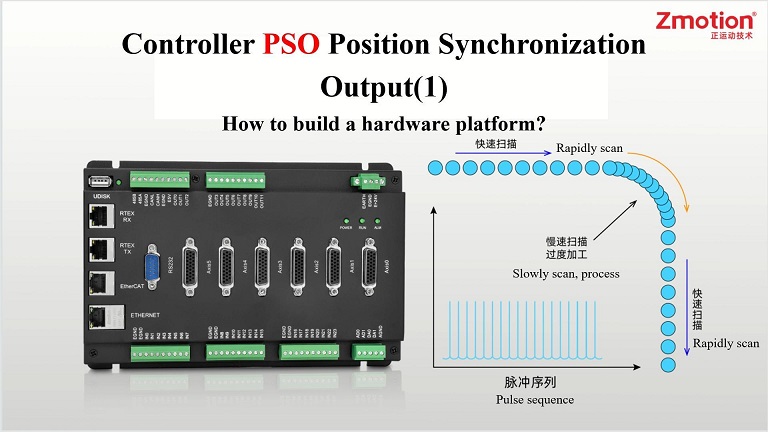
Position synchronous output PSO function is required, which means
hardware should support PSO function. That is, select the motion controller that is with PSO function and with required axes for actual applications.
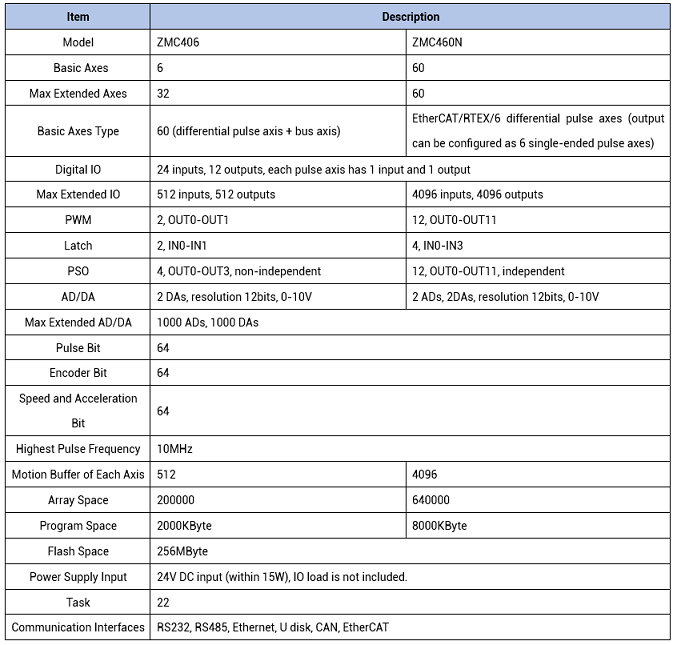
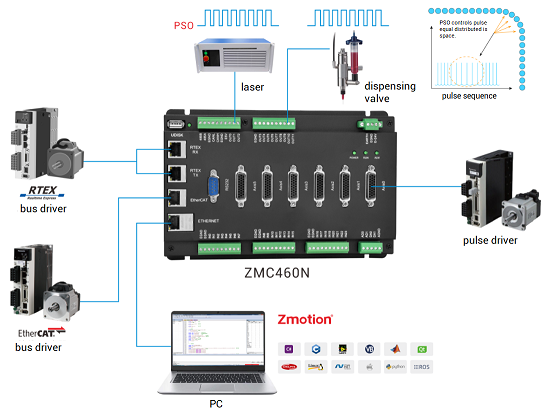
In Zmotion, there are several series of motion controllers. Of course, some support position synchronized output function, for example, ZMC406 bus EtherCAT motion controller, ZMC460N dual-bus (EtherCAT & RTEX) bus motion controller, etc., and here, take these two motion controllers as examples to describe the hardware comparison output function.
Therefore, let's know more about
ZMC406 and ZMC460N controllers.
ZMC406
bus controller is a 6-axis network motion controller, there are 6 pulse axes interfaces, which include differential pulse output and differential encoder input. And 32 axes can be reached through expansion module. It also supports usage of mixing pulse driver and EtherCAT bus driver.
ZMC460N
is a kind of dual bus controller, whose resources are more than ZMC406. It comes with 60-axis, also has 6 pulse axes. In addition, EtherCAT bus axis, RTEX bus axis and pulse axis can be used together. For general outputs, they can be configured as single-ended pulse output. For general inputs, they can be configured as single-ended encoder.
For position synchronous output function:
ZMC406 supports
4-channel PSO outputs, and
they are not independent
, which means 4-channel can not output at the same time, each system period only can
output once. Therefore, it is usually applied in single-comparison occasions.
ZMC460N supports
12-channel PSO outputs,
they are independent.
Then it can compare
multiple times in one cycle. In many applications, it can meet requirements.
These two controllers are high-performance controllers, both are with powerful functions, linear interpolation, continuous interpolation, circular interpolation, space arc, helical interpolation, electronic cam, electronic gear, position latch, synchronous follow, virtual axis configuration, hardware comparison output, hardware timer, precision output in motion. And real-time motion control can be achieved through optimized network communication protocol. In addition, EtherCAT or CAN bus expansion modules can be used to extend axis resources.
As for development, they are programmed by
Zmotion ZDevelop or
host PC (VC, VB, VS, C++Builder, C#).
While debugging through host pc, it also can connect to controller by ZDevelop, in this way, dynamic library "zmotion.dll" is required.
Here, ZDevelop is used.
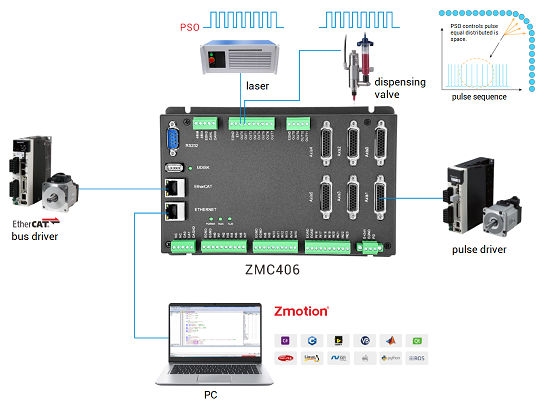
PSO hardware comparison output function uses high-speed IO, the respond frequency is 1MHz, and the respond speed can be up to us level.
More controller specification parameters can be checked through "?*max" in ZDevelop.
"?*set"
can view instruction parameter values.
"?*port"
can view communication channels.
--ZMC406--
--ZMC460N--
Position Synchronization Output PSO Function
Position synchronized output function is used to
compare real-time captured encoder measurement position (pulse position can be used when there is no encoder)
and position set by comparison mode, then control OP to output signals synchronously at high-speed.
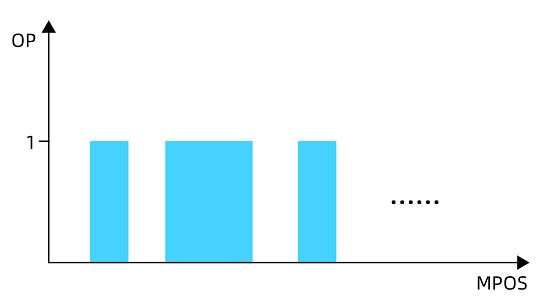
Generally, PSO function outputs signals synchronously with the laser (or dispensing spraying valve devices) to synchronize phases. In motion trajectory all stages
(acceleration, deceleration and constant speed)
, trigger output switch in constant space or constant time to achieve that pulse energy are distributed in processed object.
"Position synchronization output" function ensures high-speed and stable output signals, in whole motion trajectory
, trigger output signal with fixed distance, no need to consider the whole speed due to high enough output precision.
Specifically, in linear part, it is with rapid speed. In fillet deceleration part, it ensures constant space output. Usually, fillet processing part occupies a small part in whole processing process, which means processing effect is ensured and production can be promoted at the same time.
Position Synchronization Output Commands
PSO hardware comparison output function is mainly achieved by
"HW_PSWITCH2", "MOVE_HWPSWITCH2" and "HW_TIMER".
Former two commands are used
to set the distance of triggering comparison output
. The last one is used
for hardware timer
, which can be matched with former to control pulse width precisely.
(1) HW_PSWITCH2 -- Hardware Position Comparison Output
Instruction Description:
Through setting comparison conditions, control OP port to high-speed output signals continuously, and please note
controller must be with output port that supports hardware comparison output.
For example, ZMC406 can use OUT0/1/2/3, ZMC460N can use OUT0-OUT11.
It can compare pulse axis position, encoder measurement position and bus axis position.
And the comparison position is set by ATYPE. When it compares main axis that is with encoder input, automatically using encoder position to trigger, when no encoder, comparing pulse output.
If needs to adjust output precise time,
"MOVEOP_DELAY" can be used.
Notes:
--
for general controllers, each system cycle can only compare once, which can be checked through "SERVO_PERIOD". But when system period is too large, and comparison output pulse width is less than system cycle, it will cause abnormal output. For some controllers, ZMC460N, ZMC504SCAN, multiple comparison can be achieved by one system cycle.
--"HW_PSWITCH 2" command and "MOVE_OP" precision command use same hardware resources,
it is not recommended to use them at the same one channel, but they can be used in different channels synchronously.
--While calling
TABLE position data, don't modify TABLE before completing all comparison points.
--While using pulse motors, measurement position (MPOS) is compared only when ATYPE is 4. If ATYPE is 1/7 (default), command position (DPOS) is compared.
Instruction Grammar:
HW_PSWITCH2(mode, [...])
Different modes need to fill in different parameters, below shows 2 simple examples, for more, please refer to ZBasic manual.
A. Mode = 1: single-axis comparison
Mode=1: single axis comparison
HW_PSWITCH2(1,opnum,opstate,tablestart,tableend[,Direction])
mode: 1-open comparer
opnum: relevant outputs
opstate: output status of the first comparison position
tablestart: TABLE No. that saves the first comparison point's absolute coordinate
tablesend: TABLE No. that saves the last comparison point's absolute coordinate
direction: the first coordinate to judge direction, 0-negative, 1-positive, -1-no direction used.
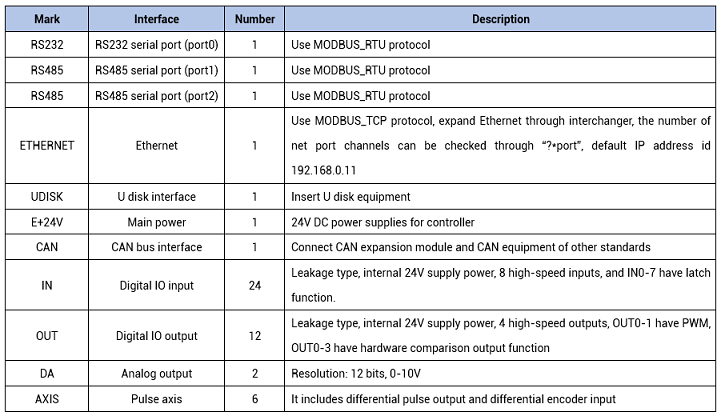
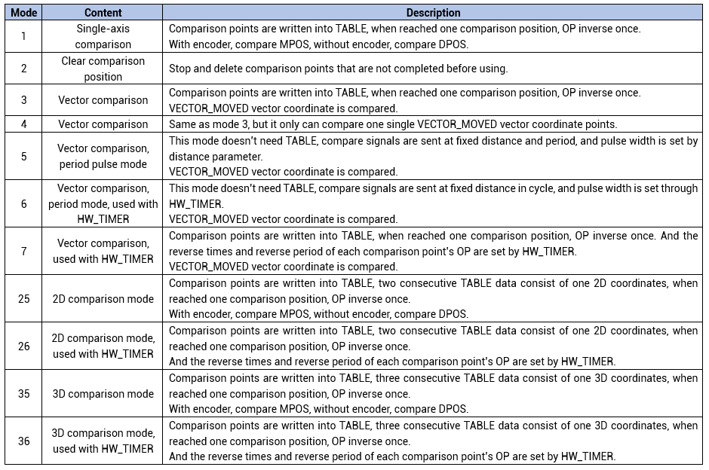
This mode is very easy. It needs TABLE register to save position coordinates that requires comparison output, then under PSO control, when reaching one comparison point position, it will inverse it, until all coordinates completed. Please refer to below image, it shows 6 comparison points' OP output, P means comparison point.
For example: mode=1, single-axis mode, compare positions in TABLE
BASE(0)
ATYPE=0
UNITS=10000/10
SPEED=100
ACCEL=1000
DECEL=1000
SRAMP=100
DPOS=0
MPOS=0
OP(0,OFF)
TABLE(0,50,100,150,200) 'comparison position coordinates configuration
HW_PSWITCH2(2) 'stop and delete comparison that not finished
HW_PSWITCH2(1, 0, 1, 0, 3,1) 'compare 4 positions, operate OUT0
TRIGGER 'trigger the oscilloscope
MOVE(300)
END
captured oscilloscope waveform: when reached TABLE four coordinates 50, 100, 150, 200, OP reverses.
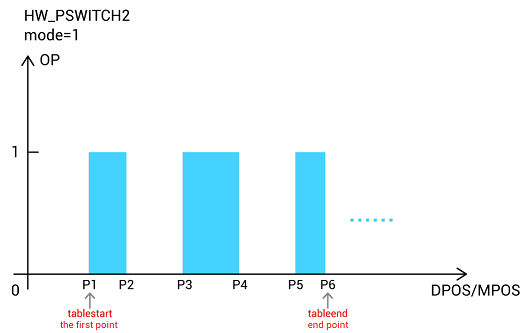
B. Mode=6: vector comparison method, cycle mode, used together with HW_TIMER
HW_PSWITCH2 (mode,opnum,opstate,vectstart,repes,cycledis)
mode: 6-open comparer
opnum: relevant outputs
opstate: output status of the first comparison position
vectstart: comparison point VECTOR_MOVED current motion distance
repes: repeat period, compare once in one cycle
cycledis: period distance, output opstate every time after cycledis
This mode doesn't need TABLE, it only needs to specify the
"VECTOR_MOVED" of the first trigger position, including the times of comparison period, the distance of each output. Then, use
"HW_TIMER" to control the pulse width and times of position output when achieves one period each time.
Below shows parameters configuration, red one is HW_PSWITCH2 instruction, orange one is HW_TIMER instruction.
And all distance involved in this mode are vector coordinates, which are used for comparison output under single-axis motion or interpolation motion mode.
For example: mode=6, period mode used together with HW_TIMER
RAPIDSTOP(2)
WAIT IDLE(0)
BASE(0)
ATYPE=1
UNITS=10000/10
SPEED=100
ACCEL=1000
DECEL=1000
SRAMP=100
DPOS=0
MPOS=0
OP(0,OFF)
TRIGGER
VECTOR_MOVED=0 'set vector initial position as 0 for viewing
HW_PSWITCH2(2) 'stop and delete comparison that not finished.
HW_PSWITCH2(6,0,1,100,4,50) 'start to compare from position 100, compare 4 times, period distance is 50, output valid time is determined by HW_TIMER
HW_TIMER(2,100000,50000,2,off,0) 'after 50ms, OUT becomes off from on
MOVE(400)
END
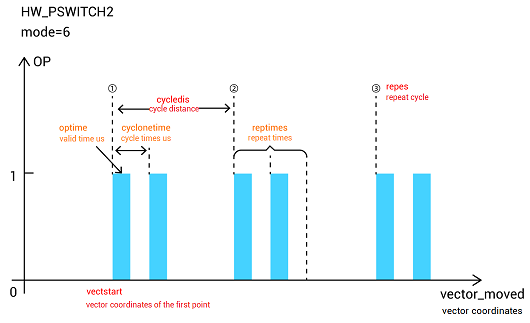
captured waveform:
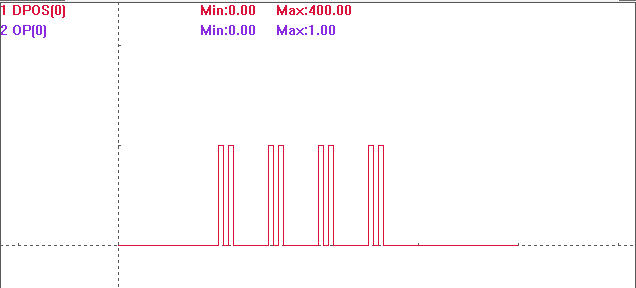
Output port is OP(0), the first comparison output status is ON
, and the vector coordinate of the first OUT is 100, compare 4 times, and trigger once when spans 50.
When each time triggered, the output time of OP is set by HW_TIMER. Here, each pulse output cycle is 100ms, valid width is 50ms, and trigger twice continuously for each comparison position.
under YT mode:
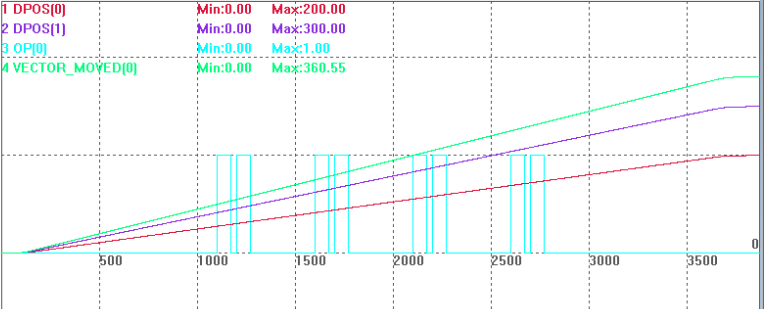
Change the single axis motion as MOVE(200, 300) two-axis interpolation, others are the same, compare combined vector position of two axes "VECTOR_MOVED".
RAPIDSTOP(2)
WAIT IDLE(0)
BASE(0)
ATYPE=1
UNITS=10000/10
SPEED=100
ACCEL=1000
DECEL=1000
SRAMP=100
DPOS=0
MPOS=0
OP(0,OFF)
TRIGGER
VECTOR_MOVED=0 'set vector initial position as 0 for viewing
HW_PSWITCH2(2) 'stop and delete comparison that not finished.
HW_PSWITCH2(6,0,1,100,4,50) 'start to compare from position 100, compare 4 times, period distance is 50, output valid time is determined by HW_TIMER
HW_TIMER(2,100000,50000,2,off,0) 'after 50ms, OUT becomes off from on
MOVE(200,300) 'two-axis linear interpolation
END
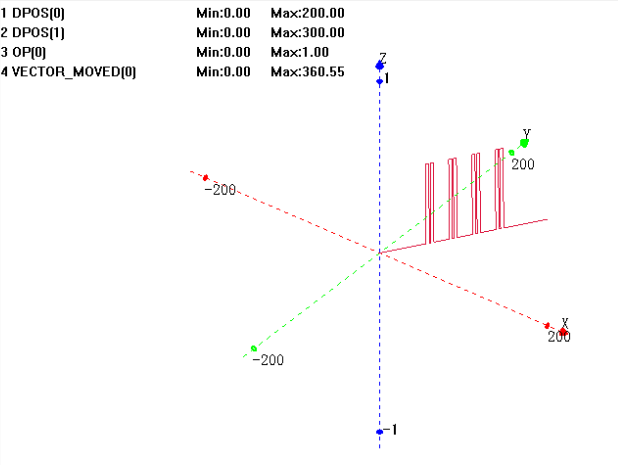
under XYZ mode:
(2) HW_TIMER -- Hardware Timing
Instruction Description:
Hardware timer is used to restore electric level after hardware comparison output for a certain time.
There is only one "HW_TIMER", and when HW_TIMER is called each time, the former calling will be stopped compulsively.
And OP and MOVE_OP can close HW_TIMER pulse that is operating,
which means HW_TIMER can be used as PWM. OP outputs, pulse output will be on, then next OP outputs, pulse output will be closed. When MOVE_OP precision output is used, infinite pulse function of precision PWM output can be realized.
Use ?*HW_TIMER to see the number of remaining pulses.
Notes:
Each period outputs signal once, and the period time must be larger than system period, otherwise, output will be abnormal. Also, used output ports must support position synchronized output function.
Instruction Grammar:
HW_TIMER(mode, cyclonetime, optime, reptimes, opstate, opnum )
mode: 0-stop, 1-run
cyclonetime: cycle time, us is the unit
optime: valid time, us is the unit
reptimes: repeat times, start the mode, when reptimes=0, HW_TIMER will be softly closed, and uncompleted pulses will keep outputting.
opstate: output default status, start to do timing when output port is not current state
opnum: output NO., the port must support hardware comparison output.
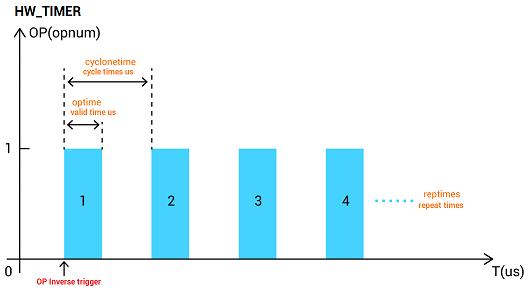
For example:
RAPIDSTOP(2)
WAIT IDLE(0)
BASE(0)
ATYPE=1
UNITS=100
SPEED=100
ACCEL=100
DECEL=100
DPOS=0
TRIGGER
DELAY(100)
OP(0, OFF)
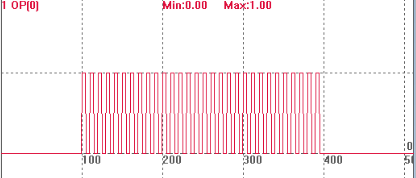
HW_TIMER(2, 10000, 5000, 30, OFF, 0) 'after OUT0 is changed to ON, hardware timer is triggered to do timing, the cycle is 10ms, after 5ms, it becomes OFF, until 30 times.
OP(0, ON) 'trigger timing
END
Please refer to below captured OP(0), the period is 1ms, which means the time unit is 1ms. After delay 100ms, it starts to trigger OP high-speed output, the total time is "10000us*30". The third parameter is used to adjust output pulse's width.
(3) MOVE_HWPSWITCH2 -- Hardware Comparison Output in Buffer
This command's function and usgae are same as "HW_PSWITCH2",
the difference is that this command enters motion buffer, that is, execute comparison in buffer.
Command Video Description, Welcome!